Parse & Replace
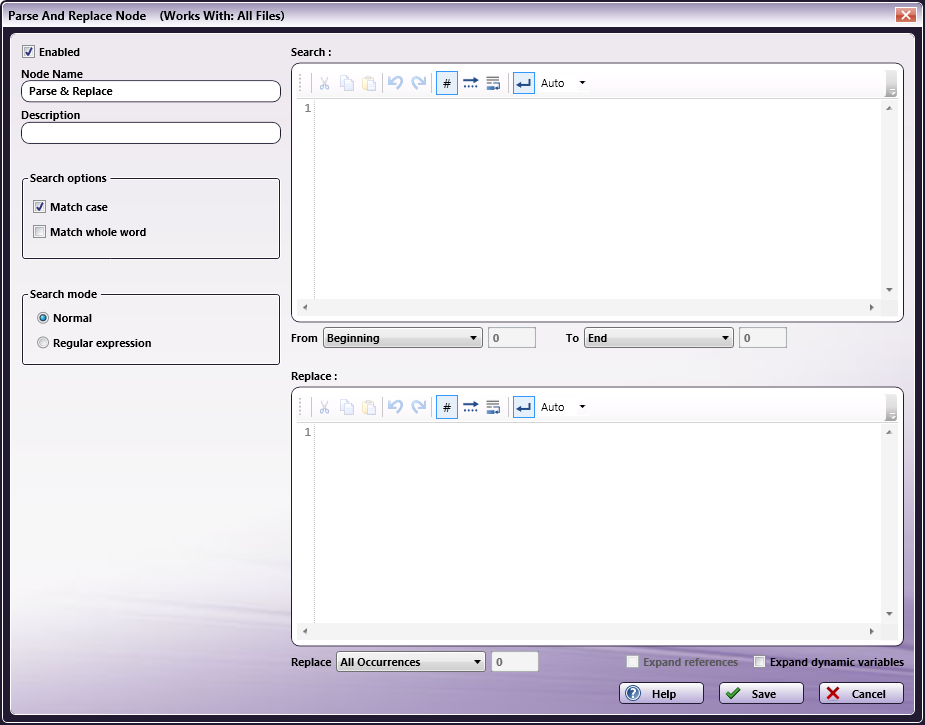
The Parse & Replace function is used to replace a keyword or phrase into a file after meeting your Search criteria. You need to specify the search criteria in the upper portion of the window, and then use the lower section to define where and when to replace the text string.
Note: This process can be used with any files that have been converted to PS, PCL, or PRN file types. In addition, this process works with text files.
To open the Parse And Replace Node window, add a process node for Parse & Replace and double-click on it.
-
Check the Enabled box so that the process will be run. When unchecked, this process will be ignored. Documents will pass through as if the node was not present (i.e., continue along the default or ‘positive’ path). Note that a disabled node will not check for logic or error conditions.
-
In the Node Name field, enter a meaningful name for the Parse & Replace node.
-
In the Description field, enter a description for the Parse & Replace node. Although this is not required, it can be helpful to distinguish multiple processes from each other. If the description is long, you can hover the mouse over the field to read its entire contents.
-
In the Search options area, do the following:
-
Check the Match case box to include in the results file names which match the case specified.
-
Check the Match whole word box to include in the results only the whole word specified.
-
-
In the Search mode area, specify either:
-
Normal to search the file name for the exact text entered.
-
Regular expression to use regular expressions to search for a pattern, rather than just words or phrases.
-
-
In the Search for area, enter the text string or expression that you want to use as your search criteria; then specify the START and END points for your search in the From and To fields. Options include:
| From | To |
|---|---|
| Beginning | End - Search from the beginning of the file to the end of the file being parsed. |
| Line Number - Search from the beginning of the file to a specific line number; enter a line number in the blank field provided. | |
| First Occurrence - Search from the beginning of the file to the first occurrence of a match. It will always return only one match. | |
| Last Occurrence - Search from the beginning of the file to the last occurrence of a match. It will always return only one match. | |
| Occurrence Number - Search from the beginning of the file to a specific occurrence within the results. This field can accept a negative number to search up to an occurrence that is a certain number from the last occurrence. For example, if you specify -5 in this field, you will search up to the fifth occurrence from the last. It will always return only one match. | |
| Line Number | End - Search from a specific line number (entered in the blank field provided) up to the end of the file being parsed. |
| Line Number - Search from a specific line number (entered in the blank field provided) to a specific line number (entered in the blank field provided). | |
| First Occurrence - Search from a specific line number (entered in the blank field provided) to the first occurrence of a match. It will always return only one match. | |
| Last Occurrence - Search from a specific line number (entered in the blank field provided) to the last occurrence of a match. It will always return only one match. | |
| Occurrence Number - Search from a specific line number (entered in the blank field provided) to a specific occurrence within the results. This field can accept a negative number to search up to an occurrence that is a certain number from the last occurrence. For example, if you specify -5 in this field, you will search up to the fifth occurrence from the last. It will always return only one match. | |
| All Previous Occurrences* | First Occurrence - Search within all of the matching blocks of content within previous results up to the first occurrence of a match. It will always return only one match. |
| Last Occurrence - Search within all of the matching blocks of content within previous results up to the last occurrence of a match. It will always return only one match. | |
| Occurrence Number - Search within all of the matching blocks of content within previous results up to a specific occurrence within the results. This field can accept a negative number to search for an occurrence that is a certain number from the last occurrence. For example, if you specify -5 in this field, you will search to the fifth occurrence from the last. It will always return only one match. | |
| All Occurrences - Search within all of the matching blocks of content within previous results up to all occurrences of a match. | |
| * The All Previous Occurrences option only works if the previous rule was a “Search for” operation and the matching results are your Start point. |
-
In the Replace with area, enter the text string that should replace a keyword or phrase at a position which you specify within a file. Replace options include:
-
All Occurrences: Replace a word or phrase at all occurrences of a match.
-
First Occurrence: Replace a keyword or phrase at the first occurrence of a match in your search results, with a new word or phrase.
-
Last Occurrence: Replace a keyword or phrase at the last occurrence of a match in your search results, with a new keyword or phrase.
-
Occurrence Number: Replace a word or phrase at a specified occurrence of a match to your search results, with a new word or phrase. This field can accept a negative number to replace at an occurrence that is a certain number from the last occurrence. For example, if you specify -5 in this field, you will replace the fifth occurrence from the last.
-
Select the Save button to keep your Parse & Replace definition, and add transitions to the next step in the workflow. You can also select the Help button to access online help and select the Cancel button to exit the window without saving any changes.
-
Expand References
When you use regular expressions in your search operation, you can replace the result of your search with the value of a specific reference group by using the Expand References checkbox.
To replace text with values from regular expression reference values, you can use the following syntax:
(\ )
or
g< > (when referencing friendly names or subgroup numbers)
Examples
The examples below use the following text file as the file being processed:
%KDKBody: (Letter) on
%KDKPrintMethod: print
%KDKOutputMedia: stapler
%%Requirements: numcopies(2) staple(front) fold(none) duplex(on) collate jog(alternate)
%KDKRequirements: numcopies(2) staple(front) fold(none) duplex(longedge) collate jog(alternate) trim(off)
%KDKCovers: (Letter) none
%KDKRotation: 0
%KDKError: on (Letter)
%KDKPeSubset: 1 6
%KDKPeOutput: stapler 6
To replace the “KDK” string with “KM” yet keep all the other values in each command line, do the following:
-
On the Parse and Replace node, click the Regular Expression radio button in the Search Mode area.
-
Enter the following regular expression in the Search area:
^%KDK(.+):(?<Value1>.+)$
-
Enter the following in the Replace area:
KM%\1:\g<Value1>
-
Make sure that the Expand References box is checked.
-
If the Replace All Occurrences option was chosen, the result would be as follows (with the replaced text highlighted in red):
KM %KDKBody: (Letter) on
KM%PrintMethod: print
KM%OutputMedia: stapler
KM%Requirements: numcopies(2) staple(front) fold(none) duplex(longedge) collate jog(alternate) trim(off)
KM%Covers: (Letter) none
KM%Rotation: 0
KM%Error: on (Letter)
KM%PeSubset: 1 6
KM%PeOutput: stapler 6
Expand Dynamic Variables
As well as expanded references, you can also choose to replace text with expanded dynamic variables during your Parse and Replace operation by checking the Expand Dynamic Variables box. You can also specify anything that was previously captured as metadata in the workflow, such as barcodes and OCR zones.
Example: To replace text with the file name and extension, you could add {file:fullname} in the Replace area.
Using the Tool Bar
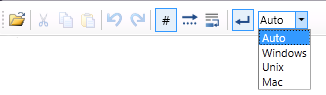
Using the tool bar, you can do the following:
-
Load Text - Loads text from another file. You will be directed to a window where you can find and select the file to be loaded. Note that the file size should not exceed 2 MB.
-
Cut - Moves text to clipboard.
-
Copy - Copies text to clipboard.
-
Paste - Pastes text from clipboard.
-
Undo - Reverses the last action performed.
-
Redo - Repeats the action that had previously been “undone.”
-
Line numbers - Displays/hides line numbers.
-
White spaces/tabs - Displays/hides white spaces and tabs.
-
Text wrap - Keeps the text in the viewable area.
-
Line ends - Displays/hides markers signifying the end of the line.
-
Custom line ends - Choose what kind of markers to use to specify line endings from now on when inputting text: Windows, Unix, or Mac.
Note: After completing the Insert operation, all of the “Search For” results are cleared.

